Organizational Behavior Management Terms for BCBAs
Understanding Organizational Behavior Management as an ABA Subspecialty
Behavior analysis evolves quickly. BCBAs now focus on team dynamics alongside client care. Organizational Behavior Management (OBM) applies ABA principles to workplaces. It shifts from individual therapy to group behaviors.
OBM analyzes antecedents, behaviors, and consequences in organizations. This influences productivity and safety. BCBAs extend functional behavior assessment (FBA) skills to staff. Interventions must follow BACB Ethics Code standards.
The Journal of Organizational Behavior Management defines OBM as assessing and changing work environments to improve employee performance (OBM in Journal). It stresses observable, measurable shifts. BCBAs use data collection and reinforcement here. OBM tackles ABA in the workplace problems, like consistent protocols in clinics. This cuts errors and boosts client progress.
OBM adapts well to sectors like healthcare and education. Studies show OBM interventions enhance staff adherence to evidence-based practices (OBM as Management Supplement). This supports client goals. In supervisory roles, OBM terms help BCBAs lead teams.
Key Takeaways for BCBAs
- OBM extends ABA to improve team performance and culture.
- Pinpointing and data measurement make interventions precise.
- The B-A-S-I-C model guides systematic workplace changes.
- Reinforcement and antecedents drive sustainable results.
- Ethical integration boosts documentation and reduces errors.
Essential Organizational Behavior Management Terminology for BCBAs
Organizational Behavior Management terminology BCBA experts use builds on ABA basics. These terms bridge clinical and organizational work. They aid clear communication and intervention planning. This avoids vague performance talks.
Pinpointing means defining behaviors in observable, measurable ways. It helps track and improve them. Pinpointing turns broad goals like "better teamwork" into targets. For example, "finish handoffs in 2 minutes, 90% of shifts."
This stems from ABA's operational definitions. BCBAs baseline performance first. Then, they target changes.
Performance measurement collects and analyzes behavior data. It checks organizational success. Tools include frequency counts and interobserver agreement. This ensures reliable results.
The OBM Network notes that good measurement spots gaps between current and ideal performance. It directs focused fixes (OBM Network Overview).
Other terms link in. Performance matrix maps behaviors to results visually. It shows how staff accuracy affects session quality. Feedback loop cycles data into adjustments. Timely input reinforces gains, like ABA principles.
These tools let BCBAs blend ABA in the workplace smoothly.
The OBM Basic Process Model: Breaking Down B-A-S-I-C
The OBM basic process model uses B-A-S-I-C. It helps BCBAs diagnose workplace behaviors step by step. This adapts ABA problem-solving to organizations. Interventions stay evidence-based and lasting.
Core parts follow sequence, per behavioral systems analysis. Start with Behavior specification (B). It's like pinpointing. Define targets clearly. Measure baselines, such as RBT note completion rates.
Then, Analysis (A). Do FBA for OBM. Spot triggers like heavy workloads or poor instructions. Understand behavior causes.
Strategy development (S) designs plans. Use ABA tools, like reinforcement schedules. A BCBA might pick praise to raise compliance.
Implementation (I) rolls out the plan. Use feedback and training. Monitor to lock in changes.
Check (C) reviews data. Adjust as needed. The OBM Network says this loop matches therapy progress checks (OBM Process Guide).
B-A-S-I-C fits ABA in the workplace well. BCBAs build performance plans. Document each step for compliance.
Behavioral Concepts in OBM: Reinforcement, Antecedents, and Consequences
OBM draws on ABA basics to boost performance. It expands BCBA skills. Reinforcement schedules use fixed or variable ratios. They encourage steady actions, like rewarding quota hits.
Antecedent control tweaks cues to spark good behaviors. Visual checklists cut session errors. Antecedents might streamline workflows to avoid slips (Aurora OBM Principles).
Consequences guide behaviors via outcomes. Focus on reinforcement, not punishment, per BACB ethics. Praise for good reports lifts morale.
These build OBM interventions. They handle ABA in the workplace fully. Antecedent tweaks plus reinforcement aid retention in health settings (OBM Applications Review).
Integrating OBM into BCBA Documentation and Practice
Organizational Behavior Management terminology BCBA use makes documentation strategic. Performance plans detail behaviors, baselines, and metrics. They meet HIPAA standards in tools like Praxis Notes.
This lifts team performance. It clarifies supervisory roles. Embedding OBM builds lasting cultures. It cuts burnout and raises service quality (OBM Burnout Impact).
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between OBM and traditional management approaches?
OBM uses data-driven ABA like reinforcement and FBA. It skips intuition or top-down control. The OBM Network explains environmental tweaks for measurable shifts. This raises engagement (OBM Network Differences). Traditional ways ignore antecedents. Results last less.
How does pinpointing improve performance in OBM?
Pinpointing sets behaviors for exact tracking. BCBAs measure progress clearly. It cuts vagueness. Interventions hit specifics like error rates. Studies show significant productivity gains.
Can OBM be applied to small ABA clinics effectively?
Yes. OBM works in small spots with basic tools. Feedback loops train staff simply. The BACB notes its fit for tight resources. It improves culture and integrity (BACB OBM Versatility).
What role does ABA play in reducing workplace absenteeism via OBM?
ABA in the workplace via OBM checks antecedents like stress. It reinforces attendance with rewards. Journal research shows drops in absenteeism by fixing roots (OBM Absenteeism Study).
How does the B-A-S-I-C model integrate with FBA in OBM?
B-A-S-I-C builds on FBA. It adds organizational steps to plans and checks. Aurora calls it ABA tailored for work. It ensures full change (Aurora B-A-S-I-C Integration).
What industries benefit most from OBM principles?
Healthcare, manufacturing, and education gain reported benefits. OBM boosts safety and efficiency. It aligns staff with goals in ABA clinics.
Pulling together OBM's key elements, BCBAs get tools to lift ABA in the workplace. Use precise terms and B-A-S-I-C. This hits metrics and builds ethical spaces. BACB standards back it.
Implications cover fewer errors and better retention (OBM Retention Evidence). Start by pinpointing a team habit. Plan a basic fix. Review weekly data. Add OBM to docs with templates. Get BACB training. Organizational Behavior Management terminology BCBA skills let you drive real change. It amps professional reach and client wins.
Popular in Study Guides & Exam Prep
- 1
2025 RBT Competency Assessment Preparation Checklist
4,14810 min read - 2
BCBA Ethical Decision-Making Model: 8-Step Exam Guide
1,3748 min read - 3
Essential BCBA Supervision Contract Requirements
1,2659 min read - 4
RBT Task List A-01: Prepare for Data Collection — 7-Step Checklist
1,2606 min read - 5
RBT Exam Study Guide 2025: Complete Prep with Practice Questions & Tips
1,1998 min read
Popular in Study Guides & Exam Prep
- 1
2025 RBT Competency Assessment Preparation Checklist
4,14810 min read - 2
BCBA Ethical Decision-Making Model: 8-Step Exam Guide
1,3748 min read - 3
Essential BCBA Supervision Contract Requirements
1,2659 min read - 4
RBT Task List A-01: Prepare for Data Collection — 7-Step Checklist
1,2606 min read - 5
RBT Exam Study Guide 2025: Complete Prep with Practice Questions & Tips
1,1998 min read
Related Resources
Explore more helpful content on similar topics
BCBA Visual Analysis of Data: Exam Prep Essentials
Master BCBA visual analysis of data essentials for your exam. Discover how to interpret level, trend, and variability in ABA for functional relations. Ace your BCBA test with expert tips!
Philosophical Assumptions of ABA: Essential Guide for BCBAs
Explore philosophical assumptions of ABA essential for BCBAs. Discover determinism, empiricism, experimentation, replication, parsimony, and philosophic doubt with practical examples and a summary table.
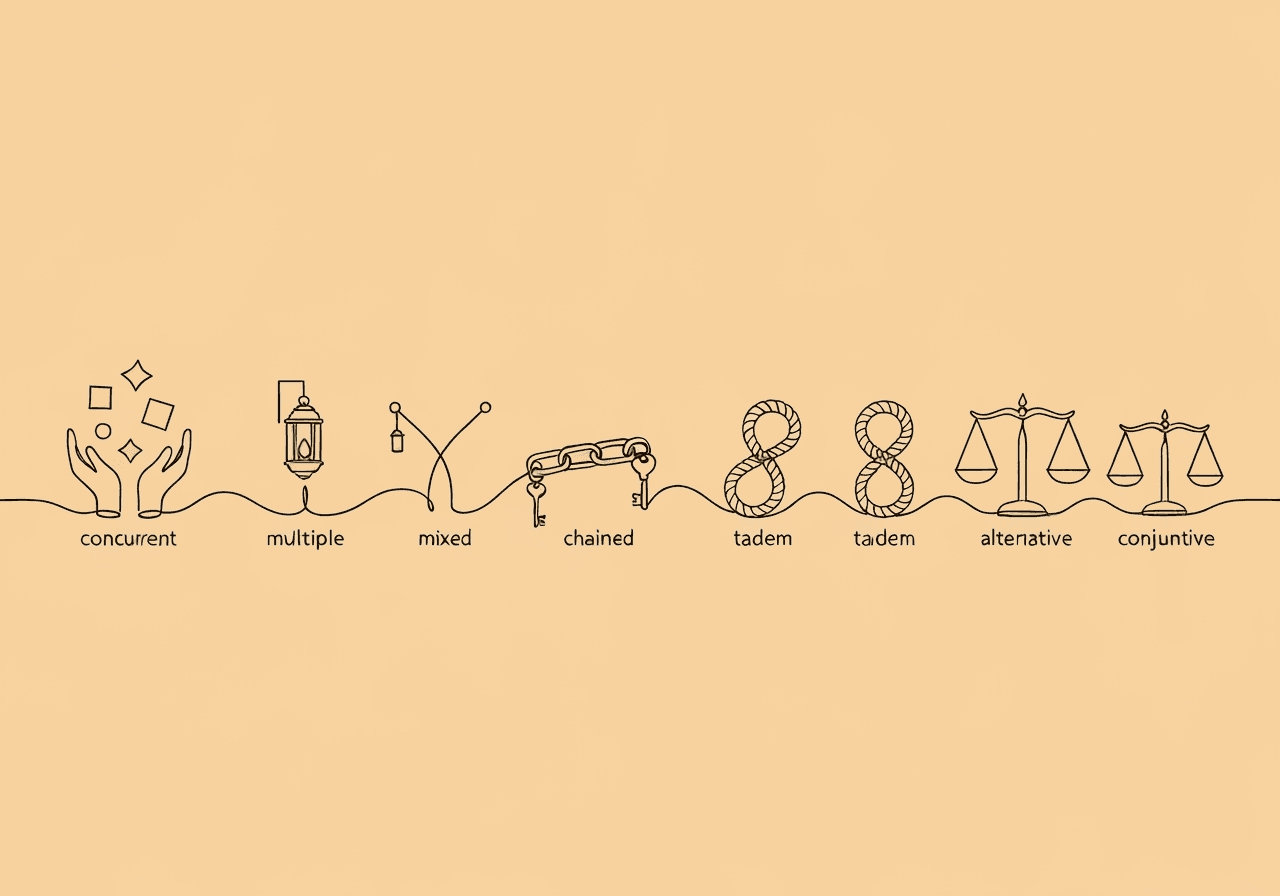
Compound Schedules of Reinforcement: BCBA Exam Guide
Master compound schedules of reinforcement for your BCBA exam. Discover the 7 types, including chained vs tandem, with clear definitions, comparisons, and tips for effective treatment design.